Understanding Your Data: Energy
Understanding our metrics and graphs relating to Energy Data
📊 Energy Metrics
Here’s a quick description for each of the four Key Stats widgets that are found at the top of your overview tab:

🌲 Carbon Emissions
Displays the total carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions generated by your energy use, converted into an equivalent number of trees per year. Useful for tracking sustainability impact and aligning with ESG goals.
⚡ Energy Use Intensity (EUI)
Measures how much energy your building uses per square metre (kWh/m²). This metric helps benchmark efficiency and compare performance across buildings or time periods. A note underneath indicates if the building is efficient or inefficient.
🔋 Energy Usage
Shows the total energy consumed (in kWh or Ah) for the selected time period. This is your core consumption metric and gives a direct view of building demand.
💵 Energy Cost
Estimates your total energy spend based on the configured tariff rate. Helps convert usage into financial terms to support budgeting and cost-saving efforts. We use a default energy rate of $0.294 kw/h
If you’d like this to show exact numbers. You will need to provide us with your standard energy rate for each property.
📊 Power Consumption Visualisation
You can view your energy data visualised in two key areas within the platform.
The first location is on the Overview tab, in the Performance Graph, just below the key metrics. This view brings together all data types from all your circuits in one central place.
By default, you’ll see a time-series chart showing power usage (kWh) across your monitored circuits, like lighting, HVAC, and mains. Each circuit is represented by a unique colour, and you can toggle between bar graph, line graph, and Sankey views depending on your preference.

Sankey Graph
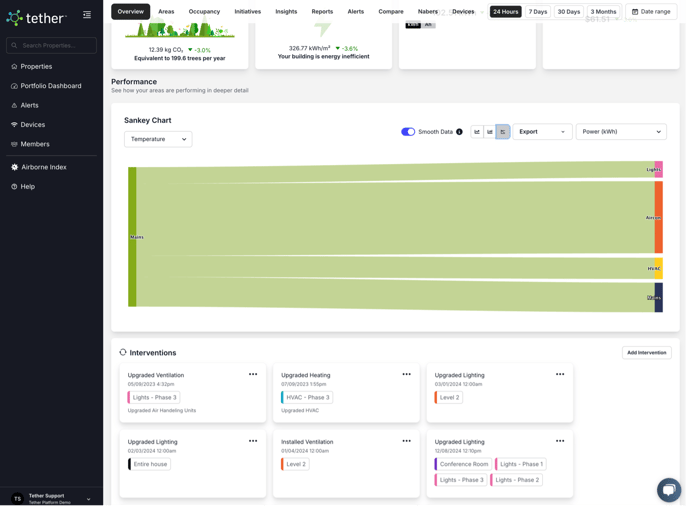
The second place is on the individual circuit page, which provides a more detailed view of a specific load. You can access this page via the Areas tab under the Energy section, or by selecting a circuit through the “Expand Filters” button on the Overview tab, then selecting the circuit.

You can also view your energy data in different formats, depending on the type of energy monitoring device you have installed.

HotDrop Data:
Power (kWh)
Total energy consumed over time, measured in kilowatt-hours — the most common metric for understanding electricity usage.
Power Cost
A monetary value based on energy consumption and your configured tariff — helps translate usage into real-world operational costs.
Power (Carbon Emissions)
Estimated CO₂ emissions generated from electricity use, typically based on grid intensity (kgCO₂/kWh) — useful for ESG reporting and sustainability tracking.
Power (Amp Hours)
Total electrical charge moved over time, measured in ampere-hours — helpful in understanding consumption from a current (rather than voltage-based) perspective.
VoltDrop Data:
Current (Max)
The highest recorded current (Amps) during the sampling period — useful for load sizing and peak demand analysis.
Current (Min)
The lowest recorded current (Amps) — often used to assess base loads or standby consumption.
Current (Average)
The average current drawn over time — a stable measure of electrical load.
Power Factor
A measure of how effectively electrical power is being used (0–1) — low values may indicate inefficiencies.
Voltage
The electrical potential supplied to the circuit — important for identifying fluctuations or under/over-voltage issues.
🔍 Zoom In on Any Time Period
If you need to focus on a specific window of time within the graph just click and drag across the chart. This will zoom in and reveal a more granular breakdown of activity for that period.
Click “Reset zoom” in the top right to return to the full view.

📉 Smooth Data Toggle
If your building uses battery-powered edge devices (like HotDrops), occasional power limitations can delay data transmission. In those cases, the data is buffered and sent later, which may present as sudden spike in the graph.
Enabling the Smooth Data toggle helps to normalise these spikes and reveal the actual trend beneath.

🧠 Circuit Filtering
Just beneath the graph you can see all visible circuits. These act as toggle filters — click any active tag to hide or reveal that data stream from the chart.
This is a simple and powerful way to isolate systems or reduce visual noise when focusing on specific loads. Any device that doesn’t track the selected data type will be greyed out.

🎨 Custom Circuit Colours
You can easily change the colours of each of the data points in the graphs.
Open show filters, and then expand and click into any circuit (e.g. Lights – Phase 1) to access more details like network type, message frequency, and firmware version. At the top, you can change the circuit’s colour, giving you flexibility to align visualisations with your reporting or internal conventions.



📈 Compare with Other Metrics
On the Performance graph located in the overview tab, you can use the Compare To menu to overlay your power data with other environmental or performance metrics — such as CO₂, occupancy, temperature, or even mould risk. This lets you build a narrative around what’s driving your energy use.

📤 Export Your Data
You can export data to support reporting, compliance, or internal benchmarking. This will export the data in a csv for the select date range you have selected
You can export data from the Performance graph on the overview tab

And also on the individual circuits graph in the circuits page, under energy tab.

📥 Exporting Data with Custom Resolutions
You can export the default resolution data from the Performance graph on the overview tab, but if you want to change the resolution (e.g. from hourly to daily or 1-minute intervals), you’ll need to do that from the specific circuit’s page, you can find it under the Areas tab, in Energy.


➡️ Interventions
The Intervention tool lets you log upgrades, maintenance activities, or operational changes — such as lighting upgrades, HVAC improvements, or insulation installs — directly into the platform.
When you add an intervention:
- It is timestamped and saved, showing what was done, where, and when.
- A marker appears on the performance graph, making it easy to see exactly when the change took place.
- This enables you to visually assess the impact of the intervention by comparing performance data before and after the change (e.g. energy use, temperature, emissions).
You can add interventions via the “Add Intervention” button, select the type, affected zones or circuits, and include notes for context.


![Tether Primary Logo-01-1.png]](https://partners.tetherhq.com/hs-fs/hubfs/Tether%20Primary%20Logo-01-1.png?height=50&name=Tether%20Primary%20Logo-01-1.png)